Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 3(111) and
3(111) and  5(0-13) grain boundaries of
5(0-13) grain boundaries of  -iron
-ironEbihara, Kenichi; Suzudo, Tomoaki
Metals, 12(4), p.662_1 - 662_10, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:32.54(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Phosphorus atoms in steels accumulate at grain boundaries via thermal and/or irradiation effects and induce grain boundary embrittlement. Quantitative prediction of phosphorus segregation at grain boundaries under various temperature and irradiation conditions is therefore essential for preventing embrittlement. To develop a model of grain boundary phosphorus segregation in  -iron, we studied the migration of a phosphorus atom in two types of symmetrical tilt grain boundaries (
-iron, we studied the migration of a phosphorus atom in two types of symmetrical tilt grain boundaries ( 3[1-10](111) and
3[1-10](111) and  5[100](0-13) grain boundaries) using molecular dynamics simulations with an embedded atom method potential. The results revealed that, in the
5[100](0-13) grain boundaries) using molecular dynamics simulations with an embedded atom method potential. The results revealed that, in the  3 grain boundary, phosphorus atoms migrate three-dimensionally mainly in the form of interstitial atoms, whereas in the
3 grain boundary, phosphorus atoms migrate three-dimensionally mainly in the form of interstitial atoms, whereas in the  5 grain boundary, these atoms migrate one-dimensionally mainly via vacancy-atom exchanges. Moreover, de-trapping of phosphorus atoms and vacancies was investigated.
5 grain boundary, these atoms migrate one-dimensionally mainly via vacancy-atom exchanges. Moreover, de-trapping of phosphorus atoms and vacancies was investigated.
Hata, Kuniki; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Hojo, Tomohiro*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 543, p.152564_1 - 152564_10, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:91.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Reactor pressure vessel (RPV) steels for pressurized water reactors (PWRs) with bulk P contents ranging from 0.007 to 0.012wt.% were subjected to neutron irradiation at fluences ranging from 0.3 to 1.2 10
10 n/cm
n/cm (E
(E  1 MeV) in PWRs or a materials testing reactor (MTR). Grain-boundary P segregation was analyzed using Auger electron spectroscopy (AES) on intergranular facets and found to increase with increasing neutron fluence. A rate theory model was also used to simulate the increase in grain-boundary P segregation for RPV steels with a bulk P content up to 0.020wt.%. The increase in grain-boundary P segregation in RPV steel with a bulk P content of 0.015wt.% (the maximum P concentration found in RPV steels used in Japanese nuclear power plants intended for restart) was estimated to be less than 0.1 in monolayer coverage at 1.0
1 MeV) in PWRs or a materials testing reactor (MTR). Grain-boundary P segregation was analyzed using Auger electron spectroscopy (AES) on intergranular facets and found to increase with increasing neutron fluence. A rate theory model was also used to simulate the increase in grain-boundary P segregation for RPV steels with a bulk P content up to 0.020wt.%. The increase in grain-boundary P segregation in RPV steel with a bulk P content of 0.015wt.% (the maximum P concentration found in RPV steels used in Japanese nuclear power plants intended for restart) was estimated to be less than 0.1 in monolayer coverage at 1.0 10
10 n/cm
n/cm (E
(E  1 MeV). A comparison of the PWR data with the MTR data showed that neutron flux had no effect upon grain-boundary P segregation. The effects of grain-boundary P segregation upon changes in irradiation hardening and ductile-brittle transition temperature (DBTT) shifts were also discussed. A linear relationship between irradiation hardening and the DBTT shift with a slope of 0.63 obtained for RPV steels with a bulk P content up to 0.026wt.%, which is higher than that of most U.S. A533B steels. It is concluded that the intergranular embrittlement is unlikely to occur for RPV steels irradiated in PWRs.
1 MeV). A comparison of the PWR data with the MTR data showed that neutron flux had no effect upon grain-boundary P segregation. The effects of grain-boundary P segregation upon changes in irradiation hardening and ductile-brittle transition temperature (DBTT) shifts were also discussed. A linear relationship between irradiation hardening and the DBTT shift with a slope of 0.63 obtained for RPV steels with a bulk P content up to 0.026wt.%, which is higher than that of most U.S. A533B steels. It is concluded that the intergranular embrittlement is unlikely to occur for RPV steels irradiated in PWRs.
 5 grain boundary of
5 grain boundary of  -iron
-ironEbihara, Kenichi; Suzudo, Tomoaki
Proceedings of Joint International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications + Monte Carlo 2020 (SNA + MC 2020), p.65 - 69, 2020/10
Phosphorus (P) is known as one of the elements which cause the grain boundary (GB) embrittlement in steels and its GB segregation is promoted by the increase of vacancies and self-interstitial atoms due to irradiation. Thus we have been developing the rate-theory model for estimating GB P segregation under several temperatures and irradiation conditions. Because the model does not include the trapping and de-trapping processes properly, however, the model cannot calculate GB P coverage which is measured by experiments. As for the de-trapping process, so far, we have considered the migration of a P atom in the GB region of  3 symmetrical tilt GB using molecular dynamics (MD). In the current study, we also simulated the P migration in
3 symmetrical tilt GB using molecular dynamics (MD). In the current study, we also simulated the P migration in  5 GB using MD and compared the result with that of
5 GB using MD and compared the result with that of  3. As a result, at 800K, it was found that a P atom cannot migrate in
3. As a result, at 800K, it was found that a P atom cannot migrate in  5 without vacancies while a P atom can migrate between iron atoms in
5 without vacancies while a P atom can migrate between iron atoms in  3.
3.
 -iron
-ironEbihara, Kenichi; Suzudo, Tomoaki
TMS 2020; 149th Annual Meeting & Exhibition Supplemental Proceedings, p.995 - 1002, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:60.52(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Phosphorus (P) is known as an element which causes grain boundary (GB) embrittlement in steels. In addition, GB P segregation is promoted by the increase of vacancies and self interstitial atoms due to irradiation. Thus, the diffusion rate theory model for estimating irradiation-induced GB P segregation has been developed based on the atomic processes. Since the present model does not include the trapping and de-trapping processes at GBs, however, it cannot calculate the value which is directly compared with experimental results. In this study, we simulated the migration of a P atom in the  3(111) symmetrical tilt GB. In addition, by tracking the migration of the P atom, the diffusion barrier energy was evaluated. As a result, the diffusion barrier energy was almost the same as the P segregation energy of an interstitial site in the GB, and it was found that P atoms migrate via interstitial sites in the GB.
3(111) symmetrical tilt GB. In addition, by tracking the migration of the P atom, the diffusion barrier energy was evaluated. As a result, the diffusion barrier energy was almost the same as the P segregation energy of an interstitial site in the GB, and it was found that P atoms migrate via interstitial sites in the GB.
 3(111) symmetrical tilt grain boundary in
3(111) symmetrical tilt grain boundary in  -iron
-ironEbihara, Kenichi; Suzudo, Tomoaki
Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering, 26(6), p.065005_1 - 065005_10, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.17(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Irradiation-induced grain boundary phosphorus segregation is an important factor for estimating the embrittlement of nuclear reactor pressure vessel steels, but the physical process of phosphorus migration to grain boundaries is still unclear. We numerically studied phosphorus migration toward  3(111) symmetrical tilt grain boundary in
3(111) symmetrical tilt grain boundary in  -iron using molecular dynamics. We found that, in the vicinity of the grain boundary within
-iron using molecular dynamics. We found that, in the vicinity of the grain boundary within  1 nm distance, an iron-phosphorus mixed dumbbell and an octahedral interstitial phosphorus atom push a self-interstitial atom into the grain boundary, and the phosphorus atom becomes a substitutional atom. A phosphorus vacancy complex in the region also becomes dissociated, and the vacancy is absorbed in the grain boundary without dragging phosphorus. The results claim that a novel view of the segregation process is required.
1 nm distance, an iron-phosphorus mixed dumbbell and an octahedral interstitial phosphorus atom push a self-interstitial atom into the grain boundary, and the phosphorus atom becomes a substitutional atom. A phosphorus vacancy complex in the region also becomes dissociated, and the vacancy is absorbed in the grain boundary without dragging phosphorus. The results claim that a novel view of the segregation process is required.
 -Iron Using First-Principles-Based Kinetic Monte Carlo
-Iron Using First-Principles-Based Kinetic Monte CarloEbihara, Kenichi; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Yamaguchi, Masatake
Materials Transactions, 58(1), p.26 - 32, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:38.56(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In order to evaluate grain boundary (GB) phosphorous (P) segregation in nuclear reactor pressure vessel steels under irradiation, the rate-theory model based on first-principles calculations is developed. In this study, we evaluated the diffusion coefficient of the mixed interstitial dumbbell of a P atom and an iron(Fe) atom using a kinetic Monte Carlo (kMC) simulation based on first-principles calculations. The evaluated diffusion coefficient was almost the same with the diffusion coefficient of P atoms which migrate via octahedral interstitial sites, and was much faster than that for P transport by vacancies. Furthermore, from the simulation of the irradiation induced GB P segregation using the model which was modified to include P atoms of octahedral interstitial sites, it was found that the boundary condition at GB is not valid for P atoms of octahedral interstitial sites
Ebihara, Kenichi; Kaburaki, Hideo; Itakura, Mitsuhiro
"Hagane No Kikaiteki Tokusei Ni Oyobosu Suiso No Koka To Sono Hyoka" Shimpojium Yokoshu (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2014/09
Since hydrogen(H) embrittlement is one factor causing degradation and/or fracture of steel, understanding its mechanism is required. The grain-boundary(GB) decohesion due to segregation of H is considered to cause the delayed fracture of high strength steels and the cold cracking in welding. In the model based on GB decohesion, information of strength of GBs estimated in the atomic scale is used for the estimation of strength or crack propagation in the macroscopic scale. However the modeling between the atomic and the macroscopic scales is not clear. In particular, the validity of the model using the elastic continuum around nano-cracks for stress concentration at the crack tip is not clear. Thus, we examined the difference of the stress distribution around the nano-crack which was estimated by molecular dynamics and by a continuum calculation. As a result, the discrepancy became remarkable at high strain. The stress concentration was not simulated by the elastic continuum model.
Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Komatsu, Atsushi; Igarashi, Takahiro; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Proceedings of European Corrosion Congress 2014 (EUROCORR 2014) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2014/09
In this paper, the effect of phosphorous concentration in grain boundary (GB) on intergranular corrosion (IC) progress was studied to understand GB corrosion behavior of stainless steels in boiling nitric acid solution. Phosphorus (P) added extra high purity type 310 stainless alloy was corroded in boiling nitric acid solution, and P in GB was detected by three-dimensional atom probe. IC progress considering with P profile in GB was studied by numerical simulation using cellular automaton method. As the results, we concluded that P concentration change around 1.4at% in GB of the alloy caused IC rate change in boiling nitric acid solution. The developed numerical method could simulate GB corrosion change with P distribution in GB.
Yamaguchi, Masatake; Shiga, Motoyuki; Kaburaki, Hideo
Science, 309(5741), P. 1677d, 2005/09
Geng et al. claim in their comment that the segregation energy of sulfur atoms in a nickel grain boundary should be calculated not on average as we did but incrementally. From their own calculations using the incremental binding energies, they concluded that the two-monolayer (GB0 4/4, GB2 4/4) segregation that bring about the reduction of the tensile strength by one order of magnitude has only 1% occupation possibility. However, they miss the point that there are many paths to the (GB0 4/4, GB2 4/4) configuration. In our re-examined calculations, one path has the 50% possibility of the occupation even if we use the incremental binding energies. Furthermore, there may be other paths that have larger possibility. To begin with, Geng et al.'s claims are not meaningful because the prediction of the occupation possibility using the simple McLean's model is not quantitative but qualitative. On the other hand, they claim that another two-monolayer (GB1 4/4, GB2 4/4) configuration brings about the reduction of the tensile strength by one order of magnitude. Their results may be miscalculations, because that is not the case in our re-examined calculations. Furthremore, they suggest a new mechanism of the strong decohesion due to the directional change of the Ni-S bonds. However, they do not show any clear evidence.
Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Kaburaki, Hideo; Arakawa, Chuichi
Physical Review E, 71(5), p.055102_1 - 055102_4, 2005/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:39.32(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The process of slow intergranular crack propagation was investigated by the finite element method model and it was found that branching is induced by partial arresting of a crack front owing to the geometrical randomness of grain boundaries. A possible scenario for the branching instability of crack propagation in a disordered continuous medium is also discussed.
Yamaguchi, Masatake; Shiga, Motoyuki; Kaburaki, Hideo
Science, 307(5708), p.393 - 397, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:281 Percentile:98.64(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Sulfur-induced embrittlement of nickel has long been wrapped in mysteries why and how sulfur weakens the grain boundaries of nickel and why a critical intergranular sulfur concentration is required. From first-principles calculations, we found that a large grain boundary expansion is caused by a short-range overlap repulsion among densely segregated and neighboring sulfur atoms. This expansion results in a drastic grain boundary decohesion that reduces the grain boundary tensile strength by one order of magnitude. This decohesion may directly causes the embrittlement since the critical sulfur concentration of this decohesion agrees well with experimental data of the embrittlement.
 5 (012) symmetrical tilt grain boundary; A First-principles study
5 (012) symmetrical tilt grain boundary; A First-principles studyYamaguchi, Masatake; Shiga, Motoyuki; Kaburaki, Hideo
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 16(23), p.3933 - 3956, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:86 Percentile:92.94(Physics, Condensed Matter)A series of non-transition elements bound to the Ni  5(012) symmetrical tilt grain boundary (GB) and the (012) free surface (FS) systems has been studied by first-principles calculation using WIEN2k code. The multilayer relaxations in presence/absence of the solutes are determined by the force minimization. The binding energies at some GB/FS/bulk sites including both interstitial and substitutional sites are calculated for all the non-transition elements between
5(012) symmetrical tilt grain boundary (GB) and the (012) free surface (FS) systems has been studied by first-principles calculation using WIEN2k code. The multilayer relaxations in presence/absence of the solutes are determined by the force minimization. The binding energies at some GB/FS/bulk sites including both interstitial and substitutional sites are calculated for all the non-transition elements between  H and
H and 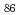 Rn. The GB/FS segregation energy is obtained by calculating the binding energy difference between the GB/FS site and the bulk site. The embrittling potency energy is obtained by calculating the difference between the GB and FS segregation energies based on Rice-Wang model. Our results show that most of the non-transition elements have negative GB/FS segregation energies. Here, this means that there exists a segregation site in the GB/FS. The embrittling potency energies are positive for most of the solutes. However, some exceptions like Be, B, C, and Si having negative and large embrittling potency can enhance the GB cohesion. Our results are found to be consistent with the experimental findings.
Rn. The GB/FS segregation energy is obtained by calculating the binding energy difference between the GB/FS site and the bulk site. The embrittling potency energy is obtained by calculating the difference between the GB and FS segregation energies based on Rice-Wang model. Our results show that most of the non-transition elements have negative GB/FS segregation energies. Here, this means that there exists a segregation site in the GB/FS. The embrittling potency energies are positive for most of the solutes. However, some exceptions like Be, B, C, and Si having negative and large embrittling potency can enhance the GB cohesion. Our results are found to be consistent with the experimental findings.
The Working Team for Examination Operation of Samples from Primary Loop Recirculation Piping at Onag
JAERI-Tech 2004-003, 74 Pages, 2004/02
The present examination has been performed with the objective to provide technical basis for identifying causes of cracking through the examination of the samples, which was conducted at the post irradiation examinations facilities of JAERI, taken from the cracked region of the recirculation pipe at the Onagawa Nuclear Power Station Unit-1. The following findings were obtained from this examination result. (1) Cracks were observed near the weld region of inner surface of the pipe and depth of the crack was about 5 to 7mm. (2) Intergranular crackings were observed in the almost whole fracture surface. Partially transgranular cracking was observed at the surface layer with the depth of about 100 m. Microstructure formed by cold work and increase of hardness were observed in these surface layers. Cracks initiated near the region where hardness value was the highest. Based on the examination results described above concerning presence of tensile residual stress by welding and relatively high dissolved oxygen contents in core coolant and so on, it is concluded that these cracks were initiated in the cold work layer of inner surface by stress corrosion cracking (SCC) and propagated along the grain boundaries.
m. Microstructure formed by cold work and increase of hardness were observed in these surface layers. Cracks initiated near the region where hardness value was the highest. Based on the examination results described above concerning presence of tensile residual stress by welding and relatively high dissolved oxygen contents in core coolant and so on, it is concluded that these cracks were initiated in the cold work layer of inner surface by stress corrosion cracking (SCC) and propagated along the grain boundaries.
Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Miwa, Yukio; Tsuji, Hirokazu; Tsukada, Takashi
Nihon AEM Gakkai-Shi, 11(4), p.242 - 248, 2003/12
no abstracts in English
Shiga, Motoyuki; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Kaburaki, Hideo
Physical Review B, 68(24), p.245402_1 - 245402_8, 2003/12
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:76.87(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Multilayer relaxations, surface/interface energies, hydrogen binding sites and energies were systematically studied using the embedded atom method (EAM), for a series of the clean and hydrogenated Ni surfaces and symmetrical tilt Ni grain boundaries. The hydrogen binding energies were in the range of 2.7-2.9 eV at the surface sites while 2.1-2.6 eV at the grain boundary sites, both being larger than at the fcc crystal interior site, 2.1 eV. These data are consistent with the conclusions from ab initio calculations that intergranular embrittlement is seen by hydrogen segregation at the Ni grain boundaries. It was found that multilayer relaxation of Ni plays a key role in trapping hydrogen at the grain boundaries.
Nishiyama, Yutaka; Suzuki, Masahide
Kinzoku, 73(8), p.48 - 52, 2003/08
no abstracts in English
Kokawa, Hiroyuki*; Shimada, Masayuki*; Wang, Z.*; Sato, Yutaka*; Sato, Yoshihiro*; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi
JAERI-Tech 2003-014, 22 Pages, 2003/03
no abstracts in English
Tsukada, Takashi
Nihon Yosetsu Kyokai "Genshiryoku Kozo Kiki No Zairyo, Sekkei, Seko, Kensa Ni Kansuru Koshukai" Tekisuto, 40 Pages, 2002/00
no abstracts in English
; Fujisaku, Kazuhiko*; *; ; Koyama, Tomozo
JNC TN8410 2001-013, 255 Pages, 2001/05
Mock-ups of acid recovery evaporators which are made of Ti-5% Ta alloy and Zr were tested under inactive condition for forty thousands hours to improve a corrosion resistance of acid recovery evaporator in Tokai reprocessing plant (TRP). The mock-up unit was designed and produced referring to the specification of acid recovery evaporator in TRP and the evaporation performance of the mock-up was 1/27 of TRP. A long-term durability of both evaporators was demonstrated by results of operation data, evaporation performance and corrosion resistance. The mock-up unit did not suffer from any trouble during the running test and the operation data such as temperature, flow, concentrations of nitric acid and metal ions were fairly stable within standard condition. As for the corrosion resistance, cracks and local corrosion such as intergranular attack were not observed on both evaporators after the running test, and a corrosion of weld was not selective. The average corrosion rates at measuring points were less than 0.1mm/yr, respectively, however, thickness of the Ti-5% Ta alloy evaporator was slightly reduced at all points of vapor phase region. In addition, from the result by test coupon, it is found that both materials have low susceptibility to stress corrosion cracking in this environment. The destructive inspection showed that the mechanical properties of both materials were not degraded during the running test. Finally, the total running time of the mock-up unit is much more than a maximum running time of acid recovery evaporator made of stainless steel in TRP (nearly 15,000 hours). On the basis of the test results, an excellent durability of Ti-5% Ta alloy and Zr evaporators under was successfully demonstrated throughout the mock-up test from an engineering perspective.
Doi, Masamitsu; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Yano, Masaya*; Sekiyama, Yoshio*
JAERI-Research 2001-020, 17 Pages, 2001/03
no abstracts in English